China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This statement, while seemingly bold, reflects a reality shaped by decades of strategic economic planning and relentless industrial growth. We’ll explore China’s journey to manufacturing dominance, examining its key sectors, global impact, and the ethical and environmental considerations that accompany its remarkable rise.
From humble beginnings, China has transformed into a global manufacturing behemoth, influencing supply chains worldwide. This transformation involved significant government investment, a massive workforce, and a willingness to adapt to global market demands. But this success story also raises important questions about labor practices, environmental sustainability, and the potential risks of over-reliance on a single manufacturing powerhouse.
China’s Manufacturing Superpower Status
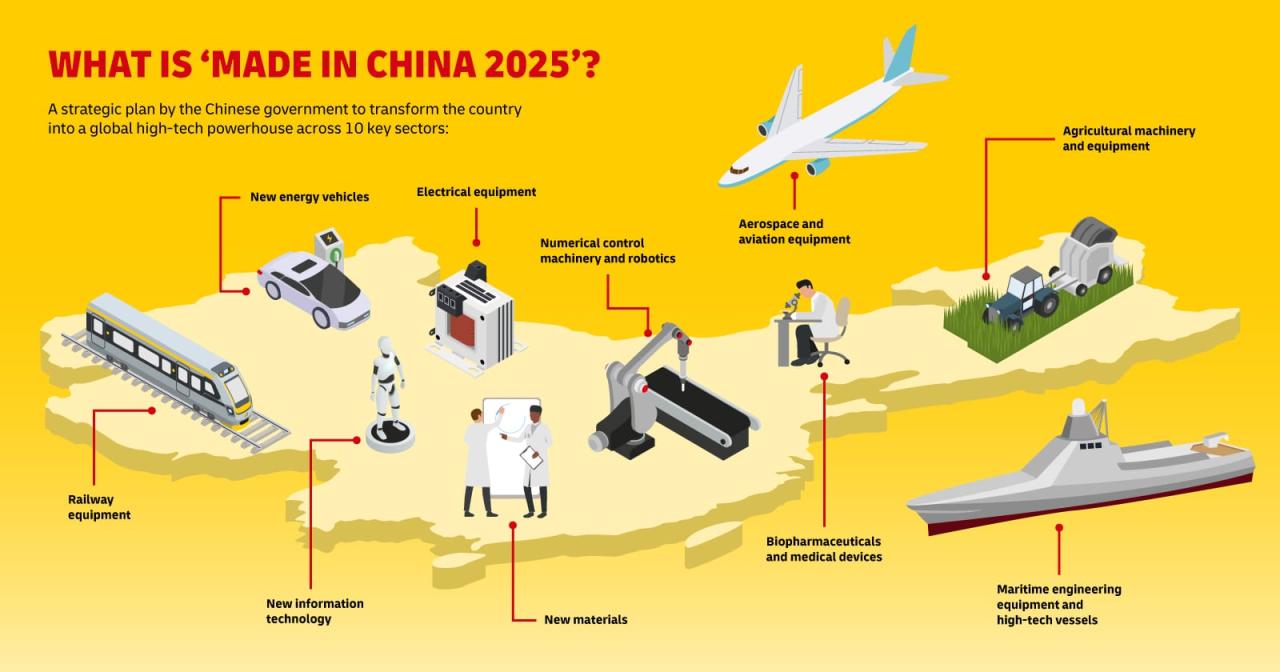
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy, China has become the global factory, impacting global trade, supply chains, and geopolitical dynamics in profound ways. This article explores the key aspects of China’s manufacturing dominance, examining its historical context, key sectors, global impact, and future prospects.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – global supply chains are incredibly complex. A major weather event like the Winter storm warning issued for Kansas City, as weekend travel to could easily disrupt shipments, highlighting just how reliant we are on efficient, often long-distance, transport. This further emphasizes China’s position; disruptions anywhere impact the global flow of goods manufactured there.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
China’s manufacturing sector’s evolution is a multi-decade journey marked by strategic policy shifts and economic reforms. Beginning with modest industrialization efforts in the post-revolutionary era, the opening up and reform policies initiated by Deng Xiaoping in the late 1970s proved pivotal. These policies attracted foreign investment, spurred export-oriented growth, and facilitated the development of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) that served as catalysts for industrial expansion.
The subsequent joining of the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001 further cemented China’s position on the global stage, granting it preferential access to international markets.
This growth contrasts with the development of other manufacturing giants. Japan’s post-war reconstruction focused on high-quality manufacturing and technological innovation, while Germany leveraged its skilled workforce and advanced engineering capabilities. The US, historically a manufacturing leader, has seen a relative decline in manufacturing’s share of its GDP in recent decades, shifting towards a more service-based economy.
| Country | GDP from Manufacturing (approx. %) | Export Volume (approx. rank) | Labor Costs (approx. rank) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 27 | 1 | Low |
| Japan | 20 | High | High |
| Germany | 22 | High | High |
| USA | 11 | High | High |
Note: These figures are approximate and can vary depending on the year and data source. The ranking is a general indicator and not precise numerical ranking.
Key Sectors of Chinese Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing prowess spans diverse sectors, each with its own strengths and challenges. Electronics, textiles, and automotive manufacturing are particularly prominent.
- Electronics: China dominates the global electronics manufacturing landscape, assembling a vast majority of smartphones, computers, and other consumer electronics. Strengths include low labor costs, extensive supply chains, and a large domestic market. Weaknesses include dependence on foreign technology and intellectual property, and concerns about environmental impact. Companies like Foxconn, a major assembler for Apple and other tech giants, exemplify China’s influence in this sector.
- Textiles: China is a major producer and exporter of textiles and garments. Its strengths lie in large-scale production capabilities, relatively low costs, and established supply chains. However, the sector faces increasing competition from other countries with lower labor costs, as well as concerns about labor practices and environmental sustainability. Many large Chinese textile companies operate globally.
- Automotive: While still catching up to established players, China’s automotive sector is rapidly expanding, both in domestic production and export markets. Strengths include a huge domestic market and government support for electric vehicle development. Challenges include technological advancements and competition from international brands. Companies like BYD and SAIC Motor are emerging as global players.
Global Supply Chains and China’s Role
China’s central role in global supply chains is undeniable. Its vast manufacturing capacity, extensive infrastructure, and relatively low costs have made it a crucial link in the production of countless goods. This reliance, however, presents both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages include lower production costs and efficient logistics. Disadvantages include vulnerability to geopolitical instability, potential for supply disruptions, and ethical concerns regarding labor practices and environmental impact. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the risks associated with over-reliance on a single manufacturing hub, causing significant global supply chain disruptions.
Technological Advancements and Innovation in Chinese Manufacturing
China is investing heavily in technological advancements to enhance its manufacturing capabilities. Automation, AI, and robotics are transforming factories, improving efficiency and productivity. While still playing catch-up in certain high-tech areas, China is rapidly closing the gap with other advanced nations through significant investments in R&D and government support for technological innovation.
The integration of these technologies is leading to “smart factories” characterized by increased automation, data-driven decision-making, and improved quality control. This trend is reshaping the global manufacturing landscape, pushing other countries to accelerate their own technological advancements to remain competitive.
Labor Practices and Working Conditions in Chinese Factories
Labor practices and working conditions in Chinese factories have been a subject of significant scrutiny. While improvements have been made, challenges remain. Typical working conditions can include long hours, relatively low wages, and limited worker protections in some sectors.
- China: Long working hours, relatively low wages (compared to developed nations), varying levels of worker protection depending on the factory and enforcement of regulations.
- USA: Generally higher wages, stronger worker protections (e.g., minimum wage, safety regulations), shorter working hours, but higher labor costs.
- Germany: High wages, strong worker protections, emphasis on worker well-being and training, but higher production costs.
Environmental Impact of Chinese Manufacturing, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News

China’s rapid industrialization has come at an environmental cost. Air and water pollution, resource depletion, and greenhouse gas emissions are significant concerns. However, the government has implemented various initiatives to address these challenges.
| Country | CO2 Emissions (approx. metric tons per capita) | Air Quality Index (AQI) (average) |
|---|---|---|
| China | 7.4 | Variable, with significant regional differences |
| USA | 14.8 | Generally better than China’s average, but with regional variations |
| India | 1.8 | Variable, with significant regional differences, often worse than China in some areas |
Note: These are approximate figures and can vary depending on the year and data source. Air quality is highly variable within each country.
The Future of Chinese Manufacturing
China’s future in manufacturing will be shaped by several factors. Maintaining its cost advantage while upgrading technology and improving labor practices will be crucial. A potential scenario involves a continued shift towards higher-value manufacturing, focusing on innovation and technological leadership in key sectors like electric vehicles, renewable energy, and advanced materials. The rise of automation and AI will further transform the industry, potentially leading to a decline in low-skilled manufacturing jobs but an increase in higher-skilled positions.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking. It’s crazy how much stuff they produce, and it makes you wonder about the long-term health impacts of all that production. For example, check out this article about the need for stronger cancer warnings on alcohol: Putting a cancer warning on alcohol is overdue, doctors say.
It’s a similar issue of widespread consumption and delayed awareness of health risks, just on a different scale than China’s manufacturing output. The global impact of both is pretty significant.
Increased domestic consumption and a focus on sustainable manufacturing practices will also play significant roles.
Challenges include rising labor costs, increasing competition from other countries, and the need to address environmental concerns. Opportunities include leveraging technological advancements, fostering innovation, and developing stronger domestic brands. The global manufacturing landscape is dynamic, and China’s role will continue to evolve, potentially leading to a more diversified global manufacturing network with multiple key players rather than a single dominant force.
Final Thoughts

China’s role as the world’s manufacturing superpower is undeniable, but its future isn’t guaranteed. Maintaining this position requires continued innovation, addressing ethical concerns surrounding labor and the environment, and navigating an increasingly complex geopolitical landscape. The coming decades will determine whether China can sustain its dominance or if a new global manufacturing order will emerge.
Detailed FAQs: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
What are some of the biggest challenges facing Chinese manufacturing in the future?
Rising labor costs, increasing automation competition, environmental regulations, and geopolitical tensions are key challenges.
How does China’s manufacturing sector compare to that of the US in terms of automation?
While the US has advanced automation in certain sectors, China is rapidly catching up, particularly in areas like robotics and AI-driven manufacturing processes.
What are some examples of Chinese companies leading in specific manufacturing sectors?
Examples include Huawei (telecommunications), BYD (automobiles), and Foxconn (electronics).
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? It’s a fascinating topic, highlighting global economics. But hey, sometimes you need a break from that kind of heavy reading; check out this hockey game recap – Call of the Wilde: Montreal Canadiens fall to Blackhawks in Chicago – for a different perspective. Then, get back to analyzing China’s manufacturing prowess and its impact on the world stage!
Is China’s manufacturing dominance sustainable in the long term?
Its sustainability depends on continued innovation, addressing ethical and environmental concerns, and adapting to evolving global economic conditions. There’s no guarantee of long-term dominance.
